Incus Project to Test 3D Printing Spare Parts in Space
Project goal is to assess the feasibility of processing scrap metals available on the moon’s surface to produce a high-quality final product via a zero-waste process.
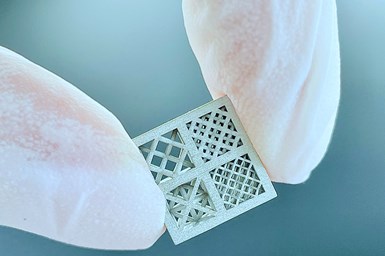
Incus’ LMM technology offers a potential solution to produce spare parts from recycled metal waste, which could enable the utilization of recycled powders from scrap metals that are available on the moon.
Incus, an Austrian provider of lithography-based solutions for additive manufacturing (AM), has partnered with the European Space Agency (ESA), OHB System AG and Lithoz GmbH in a project to develop and test 3D printing in a microgravity environment. On Earth, the Incus lithography-based metal manufacturing (LMM) process is designed to produce parts with excellent surface aesthetics and similar material properties compared to Metal Injection Molding (MIM).
One of the major challenges in maintaining a lunar station is ensuring a constant supply of goods, including spare parts. Because long-term missions have to be self-sufficient, the space experts at the ESA have shown interest in the use and reuse of both existing lunar surface materials and recycling of lunar base materials, derived from production waste and end-of-life items. The ability to manufacture necessary items and spare parts, on board and on demand, will help reduce the cost and volume of cargo missions from Earth, as well as minimize production waste.
This LMM technology offers a potential solution as it can produce spare parts from recycled metal waste, which could enable the utilization of recycled powders from scrap metals that are available on the moon. In contrast to the currently predominantly used direct metal laser melting techniques, the LMM process uses a paste or suspension as feedstock and does not rely on the use of highly spherical gas-atomized powders or support structures. The production of dimensionally accurate components separated by the thermal demolding process does not require any time-consuming, mostly manual reworking and is safe for the operator.
The goal of the 18-month project is to assess the feasibility of processing scrap metals available on the moon’s surface to produce a high-quality final product via a zero-waste process. The assessment will take into account the constraints of a space environment — for example, considering the potential contamination of the metal powder with lunar dust. Further evaluation of the influence of impurities on the sintering and result of the final microstructure will lead to optimization of the binder quantity and type, as well as the development of a sustainable manufacturing chain in space.
Related Content
-
3D Printing Brings Sustainability, Accessibility to Glass Manufacturing
Australian startup Maple Glass Printing has developed a process for extruding glass into artwork, lab implements and architectural elements. Along the way, the company has also found more efficient ways of recycling this material.
-
Castor Publishes Sustainability in Additive Manufacturing Trends Report
New research from Castor indicates manufacturers can reduce tons of carbon emissions with 3D printing.
-
Incus Successfully Tests Lithography-Based Metal Manufacturing for Lunar Environment
The project aim was to develop a sustainable process that uses lunar resources and recycled scrap metals (eventually contaminated by lunar dust) to produce spare parts on-site which could help and enhance human settlement on the moon.











