ExOne Sees Growing Industrial Use of 3D Printing Marketplaces
Items produced from orders placed through consumer 3D printing services reveal growing use of these services by non-consumers.
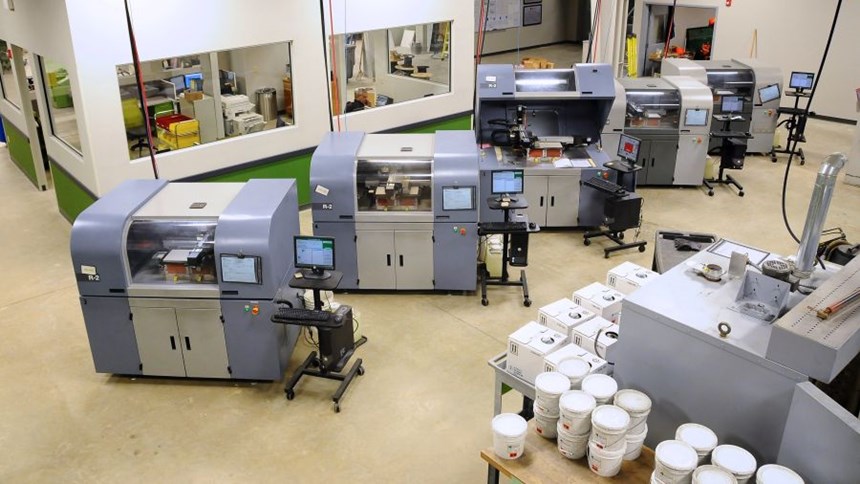
The corporate headquarters for ExOne near Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, is also the site of the company’s Production Service Center (PSC) for making metal parts. Rick Clark is the general manager of this facility, which 3D prints hundreds of parts per day on machines developed by ExOne. These additive machines use the company’s Binder Jetting process, which builds forms out of metal powder without melting the material.
Many of the parts made at the PSC are consumer items, says Clark. The reason for this is relationships the company has with 3D printing services that typically cater to consumers. Shapeways is an example—metal parts ordered though this 3D printing marketplace are often produced by ExOne. In fact, the volume of business from consumer-oriented resources such as this is so high that it accounts for 80 percent of the PSC’s part production in general, and nearly 100 percent of the activity near Christmas.
But Clark has also noticed something else—a gradual but significant change. It is no longer just consumer items he sees being ordered this way. In addition to metal jewelry and figurines, he now also sees orders, often batch orders, of what are clearly industrial components. Manufacturers are using these consumer sites as a means of uploading their component designs and obtaining metal parts.
When he first noticed this development perhaps three years ago, it was just an occasional curiosity. Not anymore, he says. He now estimates that industrial parts account for at least 15 percent of the parts ExOne sees from the online utilities.
Those parts are easy to spot, Clark says. Consumers order objects including home goods, custom pendants or hobbyist items such as ornate dice. But amidst these items in the batches of parts that ExOne runs can now also be seen brackets and machine components. One commonly recurring item is referred to by PSC staff members as the “sewing machine piece” because of its resemblance to a thread guide for a sewing machine. What this part actually does is unknown to them. Whatever function it serves, additive manufacturing seems to work as a means of producing the part, because the customer keeps ordering more.
John Baliotti is ExOne’s director of marketing and business development. He says the ability to make parts for customers by means of the PSC is an important part of almost any machine sale for the company. Binder Jetting is a distinctive process, an additive metal machine is a significant investment, and plenty of customers are still new to additive manufacturing. For all of those reasons, he says, prospective buyers generally convince themselves of the process’s effectiveness by commissioning various parts from ExOne before committing to a machine of their own.
Typically, this contract manufacturing takes the form of active engagement with the customer, including helping the customer refine the part design to take full advantage of Binder Jetting’s strengths. But now, he says, through any of various 3D printing services, it seems that manufacturers are also increasingly finding an even more basic way to begin. Consumer-focused 3D printing portals are providing industrial companies with a straightforward way to start to experiment and succeed with metal additive manufacturing.
Related Content
Additive Manufacturing Is Subtractive, Too: How CNC Machining Integrates With AM (Includes Video)
For Keselowski Advanced Manufacturing, succeeding with laser powder bed fusion as a production process means developing a machine shop that is responsive to, and moves at the pacing of, metal 3D printing.
Read MorePossibilities From Electroplating 3D Printed Plastic Parts
Adding layers of nickel or copper to 3D printed polymer can impart desired properties such as electrical conductivity, EMI shielding, abrasion resistance and improved strength — approaching and even exceeding 3D printed metal, according to RePliForm.
Read MoreThis Year I Have Seen a Lot of AM for the Military — What Is Going On?
Audience members have similar questions. What is the Department of Defense’s interest in making hardware via 3D printing over conventional methods? Here are three manufacturing concerns that are particular to the military.
Read MoreHow Norsk Titanium Is Scaling Up AM Production — and Employment — in New York State
New opportunities for part production via the company’s forging-like additive process are coming from the aerospace industry as well as a different sector, the semiconductor industry.
Read MoreRead Next
3D Printed Polymer EOAT Increases Safety of Cobots
Contract manufacturer Anubis 3D applies polymer 3D printing processes to manufacture cobot tooling that is lightweight, smooth and safer for human interaction.
Read MoreProfilometry-Based Indentation Plastometry (PIP) as an Alternative to Standard Tensile Testing
UK-based Plastometrex offers a benchtop testing device utilizing PIP to quickly and easily analyze the yield strength, tensile strength and uniform elongation of samples and even printed parts. The solution is particularly useful for additive manufacturing.
Read MorePostprocessing Steps and Costs for Metal 3D Printing
When your metal part is done 3D printing, you just pull it out of the machine and start using it, right? Not exactly.
Read More