Thermwood Adds Angle Layer Printing to Large Scale Additive Manufacturing Systems
This third print orientation for its LSAM systems enables users the ability to print at a 45-degree angle.
Share
Read Next
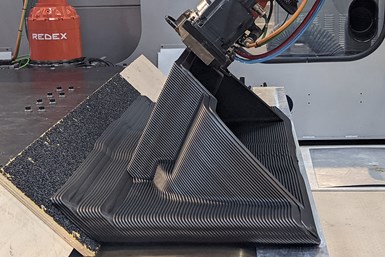
The Angle Layer Printing (ALP) option gives users the ability to print at a 45-degree angle. Photo Credit: Thermwood Corp.
Thermwood Corp. has added a third print orientation to its Large Scale Additive Manufacturing (LSAM) systems. Previously, the LSAM systems could print both horizontal and vertical layers, if equipped with the Vertical Layer Print (VLP) option, which is available on most Thermwood LSAM machines. The new addition adds Angle Layer Printing (ALP) to the VLP option, giving users the ability to print at a 45-degree angle.
According to the company, each print orientation has advantages and limitations for a particular part design, but offering all three orientations on the same machine, for the first time, means maximum print flexibility.
All print orientations use the complete LSAM printhead, including exclusive LSAM print features such as the patented compression wheel and thermal sensor layer automation. This is designed to help maintain an even layer temperature throughout the print in which the LSAM automatically adjusts the individual layer temperature to provide for superior layer fusion, the company says.
LSAM machines are currently operating in regular daily industrial production with many existing systems already equipped with VLP capability. The VLP option has been replaced with a VLP/ALP option on new machines, which offers both vertical and angle layer print capability, in addition to the standard horizontal layer print.
According to the company, the ALP option can be easily and inexpensively added to machines operating in the field that already have the VLP option. If a machine was purchased without the VLP option, the entire new VLP/ALP Print option can be added to most machines already in operation. It can be done in the field, but is a bit more involved.
Thermwood’s LSAM systems process a variety of reinforced composite polymers from room-temperature ABS and PC to high-temperature material such as PSU, PESU and PEI, which are used to produce molds and tools for the aerospace industry, patterns for the foundry industry and a variety of other applications.
Related Content
-
Sustainable Furniture Company Model No. Maintains Product Focus with Switch from DIY to Industrial 3D Printers
The startup founded in 2018 has matured in its product offerings as well as its manufacturing equipment, moving from homegrown 3D printers to industrial large-format machines.
-
BMW Group Vehicle to Adopt 3D Printed Center Console
A vehicle coming to market in 2027 will include a center console carrier manufactured through polymer robot-based large-format additive manufacturing (LFAM).
-
Video: Construction 3D Printing with Robotics, Geopolymer
Alquist 3D is aiming to revolutionize construction and infrastructure with large-format robotic 3D printing using a carbon-neutral material.










