Liqcreate Creates Flame Retardant Polymer for High Temperature Applications
Parts made with this additive manufacturing resin can withstand high temperatures without posing a fire hazard due to its self-extinguishing capabilities.
Share
Read Next
Dutch independent 3D printing material manufacturer Liqcreate has developed an engineering 3D printing resin called Liqcreate Flame Retardant HDT, which features high temperature resistance in combination with a UL94 V0 flammability rating. This rating is essential for a wide range of engineering, mobility, consumer goods and electronics applications.
The resin is an extremely rigid off-white photopolymer that can be processed on most resin-based 3D printers. The resin is compatible with digital light processing (DLP), liquid crystal display (LCD) and laser-based 3D printing systems operating in the range 385-420 nm. The 3D printing parameters for multiple printers can be found on the Liqcreate website.
Parts made with this resin can withstand high temperatures without posing a fire hazard due to its self-extinguishing capabilities. With an HDT-B value of 257°C / 495°F, it is well suite for high-temperature applications. Also, with its UL94 V0 rating, it is suitable for applications like interior parts in cars, airplanes, trains and electronic devices. In addition, it can be excellent for tooling manufacturing aids, connector housings and covers.
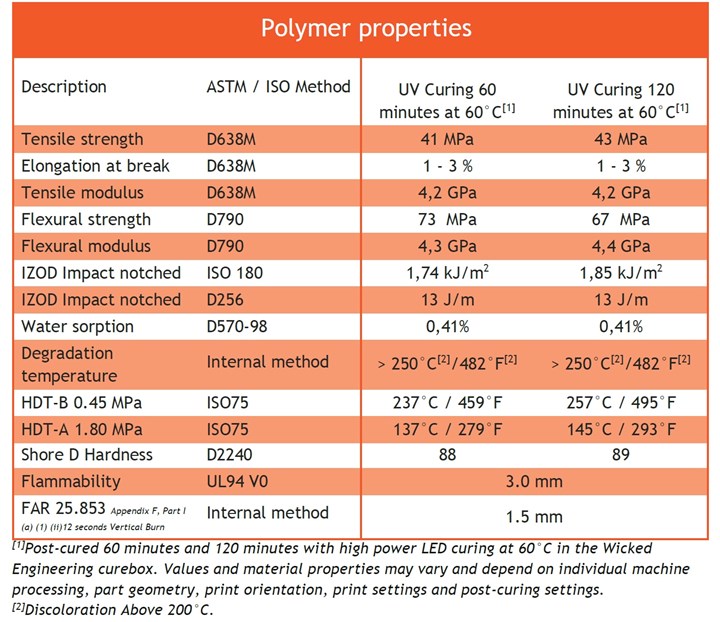
The below tables provide information regarding the mechanical properties of the Liqcreate Flame Retardant HDT:
Flame Retardant HDT Resin for Aviation and Mobility Applications
Liqcreate Flame Retardant HDT resin was tested by the UL94 organization and confirmed in their report that the product has the following flammability rating: UL94 V0 at 3mm. In addition, Liqcreate conducted an internal test method guided by the FAR 25.853 (Appendix F, Part I (a) (1) (ii)12 seconds Vertical Burn) testing methods which resulted in a pass at 1.5 mm thickness. These tests are a good basis for further development of applications within the aviation and mobility sector. Additional tests might be required to fully comply with the FAR 25.853 in aviation or the EN-45545 for train parts.
OEM Possibilities for Flame retardant 3D-Printing Resin
For OEM partners, the resin can be rebranded and optimized for different use cases and 3D printers. Alongside its branded resin range, Liqcreate also provides a custom development service, offering nonstandard formulas for specific applications. Through this service, customers can request the development of a polymer possessing precise characteristics, which impact its printing speed, as well as the properties of the resulting part.
As an independent resin manufacturer with R&D facilities, Liqcreate says it is capable of rapidly scaling its production of custom-made resins where needed. Moreover, the standalone nature of the company ensures there is minimal competition or conflict when working with 3D printer hardware manufacturers. This is said to ensure that the firm can work quickly, and get resins to market in quantity, avoiding any issues or delays that would keep clients waiting.
- Learn about a variety of polymers for additive manufacturing in our Polymer zone.
- Check out the latest advances in additive manufacturing for aerospace and automotive applications.
Related Content
Seurat: Speed Is How AM Competes Against Machining, Casting, Forging
“We don’t ask for DFAM first,” says CEO. A new Boston-area additive manufacturing factory will deliver high-volume metal part production at unit costs beating conventional processes.
Read More8 Transformations 3D Printing Is Making Possible
Additive manufacturing changes every space it touches; progress can be tracked by looking for moments of transformation. Here are 8 places where 3D printing is enabling transformative change.
Read MoreWhat Holds AM Back in Automotive Production? GM Additive Lead Describes Advances Needed
“If AM were cheaper, we would be doing more of it,” says GM’s Paul Wolcott. Various important factors relate to cost. However, the driving factor affecting cost is speed.
Read MoreThis 3D Printed Part Makes IndyCar Racing Safer: The Cool Parts Show #67
The top frame is a newer addition to Indycar vehicles, but one that has dramatically improved the safety of the sport. We look at the original component and its next generation in this episode of The Cool Parts Show.
Read MoreRead Next
Profilometry-Based Indentation Plastometry (PIP) as an Alternative to Standard Tensile Testing
UK-based Plastometrex offers a benchtop testing device utilizing PIP to quickly and easily analyze the yield strength, tensile strength and uniform elongation of samples and even printed parts. The solution is particularly useful for additive manufacturing.
Read MoreBike Manufacturer Uses Additive Manufacturing to Create Lighter, More Complex, Customized Parts
Titanium bike frame manufacturer Hanglun Technology mixes precision casting with 3D printing to create bikes that offer increased speed and reduced turbulence during long-distance rides, offering a smoother, faster and more efficient cycling experience.
Read MoreAlquist 3D Looks Toward a Carbon-Sequestering Future with 3D Printed Infrastructure
The Colorado startup aims to reduce the carbon footprint of new buildings, homes and city infrastructure with robotic 3D printing and a specialized geopolymer material.
Read More