3D printing is only one step in the overall additive manufacturing workflow. For most AM production applications, the workflow will look something like this:
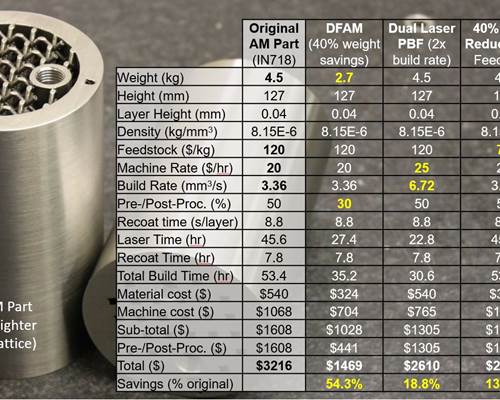
- Design the part. Design may mean modifying an existing design for 3D printing, or starting from scratch with a true design for additive manufacturing (DFAM) mindset. Computer simulation, generative design and topology optimization can all be applied to optimize the function of the part. Printing process and material selection usually occurs in the initial design step.
- Plan the build. Depending on the intended 3D printing technology, this step may entail selecting part orientation, adding support structures, packing or nesting multiple parts together, and setting printer parameters such as layer height, laser spot size, feed rate, etc.
- 3D print the part. A 3D printing build might take anywhere from minutes to days.
- Postprocess the part. Depending on the process, postprocessing could entail unpacking powder, prying or cutting parts from a build platform, cleaning, curing, heat treating, hot isostatic pressing (HIPping), etc.
- Finish the part. Many 3D printed tools and production parts will require further finishing to arrive at their completed state. Finishing steps might include machining surfaces, drilling or tapping holes, dyeing, coating or painting, and possibly welding or assembly with other parts.
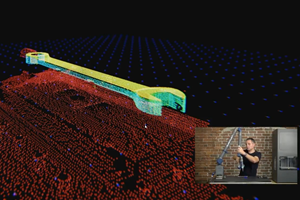
- Inspect the part. Some parts can be evaluated with CMM measurement or 3D scanning; those with complex internal features may require X-ray or CT scanning.
Different parts and applications may call for fewer or more steps. A hand tool made with fused filament fabrication (FFF) may not require any additional postprocessing once removed from the build plate. Parts with particularly stringent requirements, however, may require many more steps.
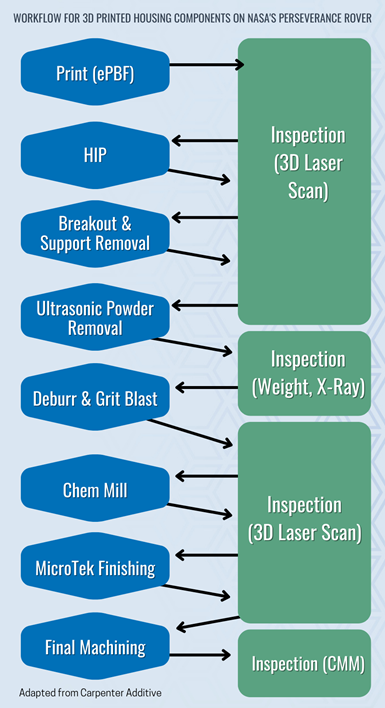
For example, the flowchart below shows the workflow for the production of five 3D printed housing components that are installed on NASA’s Perseverance rover. These lightweight, thin-walled parts required many rounds of postprocessing and inspection before they were ready for use.