As additive manufacturing (AM) continues to advance into industries ranging from aerospace to automotive to consumer goods, the people who know how to implement this technology are in greater demand. There’s no one “right” career path into additive; the technology is too new but more importantly too varied for this to be the case. AM professionals today come from all walks of life and have found their way to this space through numerous paths. But for those making a pivot or just starting out in their additive careers, there are now an expanding selection of resources that can help prepare new entrants for the job market.
If you’re looking for a career in additive manufacturing, see the links and information below on what skills you’ll need, training and education programs, and where to apply.
What Skills Does an Additive Manufacturing Professional Need?
We put this question to followers on LinkedIn and Twitter, and received responses (in both comments and private messages) ranging from technical experience to critical soft skills. Here are some of the suggested qualifications, though exact needs will vary by company and position:
- A foundation in math, at least through trigonometry
- Familiarity with CAD software; topology optimization, design for additive manufacturing (DFAM) and more can build on this foundation
- Experience with other forms of manufacturing such as CNC milling, injection molding, welding
- An understanding of materials science, whether in metals, polymers or other 3D printable materials
- Familiarity with the systems underpinning 3D printers such as lasers and motion systems, which can make printer maintenance and operation easier
- Willingness to learn; many manufacturers provide on-the-job training and keeping up with new developments is critical for most AM professionals
- Problem-solving skills, for troubleshooting difficulties, balancing priorities and negotiating challenges
- Communication skills, particularly for client-facing roles but also to support collaboration on internal teams
- Curiosity and passion!
What Programs and Certifications Are Available for Additive Manufacturing?
While formal education in additive manufacturing is not a requirement for working with 3D printing, there are a number of degree programs and certifications available now for this discipline. Many undergraduate engineer degree programs now offer tracks or coursework in additive manufacturing. More specialized programs tend to exist at the graduate level. There are also various certificate programs and training options available outside of full degree programs. The following programs are based in the U.S.:
Additive Manufacturing Degrees
- Carnegie Mellon master of science in Additive Manufacturing
- Century College associate of applied science degree in Additive and Digital Manufacturing
- Penn State master’s program in Additive Manufacturing and Design
- The Ohio State University online master’s degree in Additive Manufacturing
- University of Cincinnati master’s of engineering in Additive Manufacturing
- University of Miami master of science in Additive Manufacturing
- Westmoreland County Community College associate of applied science degree in Additive Manufacturing
Additive Manufacturing Certificates
- ASTM Personnel Certificate Program in Additive Manufacturing — Designer, QA Engineer and Technical Manager tracks
- Central Connecticut State University certificate program in Additive Manufacturing Engineering
- Cincinnati State Additive Manufacturing Technician WDC Certificate
- Colorado School of Mines graduate certificate in Additive Manufacturing
- Cuyahoga Community College certificate of proficiency in 3D Digital Design and Additive Manufacturing Technology
- Purdue University and The Barnes Global Advisors (TBGA) Additive Manufacturing Certificate program
- SME Additive Manufacturing Certification — Fundamentals and Technician tracks
- UC San Diego Extension Additive Manufacturing Certificate
- University of Maryland master’s certificate in Additive Manufacturing
Additive Manufacturing Classes and Training
- Additive Manufacturing Institute of Science & Technology (AMIST), professional training in various disciplines offered on the University of Louisville campus
- Additive Manufacturing for Innovative Design and Production, an online AM course from MIT
- America Makes Advanced Curriculum in Additive Design, Engineering and Manufacturing Innovation (ACADEMI), a “portfolio of DfAM-based courses, with a path toward industry certification”
- New Collar Digital Badges, microcertifications issued by the North American Digital Fabrication Alliance, based on self-paced classes
International programs (outside the United States)
- University of Central Lancashire (UK) master of science in additive manufacturing
- University of Nottingham (UK) master of science in additive manufacturing and 3D printing
Additive Manufacturing and 3D Printing Careers
While some businesses and startups focus exclusively on 3D printing, there are likely to be career opportunities at other existing manufacturing companies as the technology matures and adoption advances.
In addition to checking general job search sites like Indeed and ZipRecruiter, browse the sites below which cater to additive manufacturing or general manufacturing job seekers. LinkedIn is also a good job-hunting tool — search “additive manufacturing” and your desired location to get started.
Women in 3D Printing (Wi3DP) Job Board
Women in Manufacturing (WiM) Career Center
Women in Manufacturing Virtual Career Fair
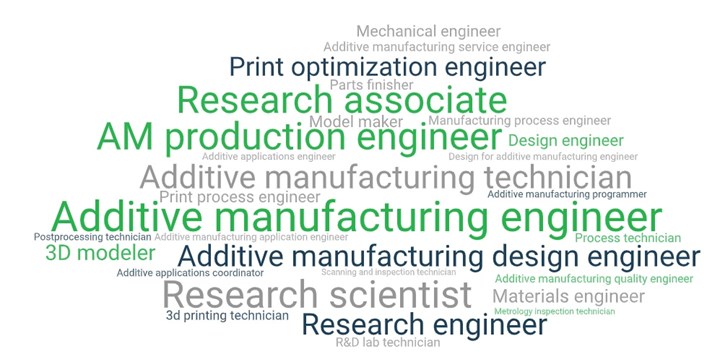
What Job Titles Do Additive Manufacturing Professionals Have?
Job titles vary widely among AM professionals, and may or may not include the terms “additive manufacturing” or “3D printing.” A survey of job listings revealed many of the most common titles, compiled into the graphic below.
The top titles are:
- AM production engineer
- Additive manufacturing engineer
- Additive manufacturing design engineer
- Research scientist
- Materials engineer
- Print optimization engineer
Related Content
How to Organize for Additive Production: AM Radio #42
Tim Simpson and Peter Zelinski discuss the next steps for succeeding with AM: After technical and process successes come the cultural, organizational and even costing considerations associated with this mode of manufacturing.
Read MoreAM 101: What Is Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)? (Includes Video)
Hot isostatic pressing has long been used for metal castings, but is now being applied as a valuable method for closing porosity in metal 3D printed parts.
Read MoreAM 101: What Is Binder Jetting? (Includes Video)
Binder jetting requires no support structures, is accurate and repeatable, and is said to eliminate dimensional distortion problems common in some high-heat 3D technologies. Here is a look at how binder jetting works and its benefits for additive manufacturing.
Read MoreUnderstanding PEKK and PEEK for 3D Printing: The Cool Parts Show Bonus
Both materials offer properties desirable for medical implants, among other applications. In this bonus episode, hear more from Oxford Performance Materials and Curiteva about how these companies are applying PEKK and PEEK, respectively.
Read MoreRead Next
6 Things I Learned about Metal 3D Printing at the AMIST
I sat in on one and a half days of a five-day class offered at the Additive Manufacturing Institute of Science and Technology (AMIST) in Louisville. Here’s just some of what I learned.
Read MoreInside the Penn State Additive Manufacturing Master’s Program, Part 1
PSU's engineering master's degree in additive manufacturing and design offers students and manufacturing professionals a higher education in a continuously maturing field.
Read MoreCrushable Lattices: The Lightweight Structures That Will Protect an Interplanetary Payload
NASA uses laser powder bed fusion plus chemical etching to create the lattice forms engineered to keep Mars rocks safe during a crash landing on Earth.
Read More

.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)