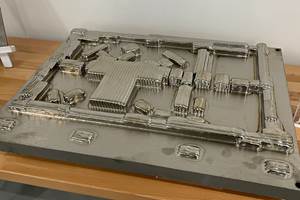
How Is Caterpillar Moving Forward with AM?
Heavy equipment manufacturer Caterpillar has found numerous uses for additive manufacturing in its operations. Here are just a few applications the company has found.
Share
Read Next
Much of additive manufacturing’s appeal comes from the long-term promise of new products, new designs and new ways of thinking about production. But that doesn’t mean there aren’t practical, effective ways to put additive manufacturing to work right now, today. While additive manufacturing for large-scale production is a ways off for almost every manufacturer, current 3D printers are well-suited for many shopfloor applications, including creating tools, gages and other manufacturing aids.
This is the approach that heavy equipment manufacturer Caterpillar has taken in its Rapid Prototyping lab, founded in 1990. Though the company has a long-term interest in using additive to produce at least some parts for its dozers, excavators and other equipment, it is taking advantage of the technology right now to make practical shopfloor tools for its own employees. The lab, now a part of the newly formed Caterpillar Additive Manufacturing Group, uses additive processes such as FDM, stereolithography and SLS to produce gages, display and scale models, assembly fixtures, hand tools, and other functional pieces for use in its own facilities. Though these aren’t end-use products, the parts the lab produces offer returns in the form of decreased costs and reduced development time due to quicker iteration turnaround. Here are just three uses the lab has found for AM in Caterpillar’s operations:
Gaging
Caterpillar has identified a number of gaging needs that can be met with custom gages 3D-printed out of plastics. For example, the company has produced field gages to measure the wear on tips, the consumable “teeth” found on the edge of an earthmover’s bucket. The gages have numbers printed directly into them, making it easy for an on-site technician to determine the level of wear on a tip. And according to Jim LaHood, Caterpillar engineering specialist for 3D printing, the plastic gages are just as accurate as metal gages and can be replaced more quickly when they wear out. A set of the field tip gages can be made overnight. They are printed in a stack of four nested together, using only $40-50 worth of plastic, for material as well as time savings.
Molds
Caterpillar molds its own silicone masking in-house. The masking includes plugs and other shaped pieces of silicone to protect holes and pockets during processes such as powder coating. Previously, employees produced the masking on makeshift molds constructed of scrap metal. The molds were heavy and sharp, and known to fail frequently. The AM Group now offers the capability to create the molds out of polycarbonate rather than metal, resulting in lighter, more reliable molds. The lab estimates that this switch has saved $27,000 per year in repairs to molds.
Production Models
Caterpillar has found value in producing 3D-printed models of parts to optimize its systems before production begins in earnest. In one example, the company created 36 ABS polycarbonate models of large forged track links (components of the chain-like link assembly found on track-type machines like dozers) in various sizes to use for machine setup and CMM programming. Normally workers would need to use heavy wood models or wait for the foundry parts themselves to arrive to perform these setup tasks. With the plastic models, employees were able to work on fixturing and CMM applications before the forged parts arrived, saving time. Completing these tasks with the lightweight ABS models was made easier by eliminating the handling of heavier parts, and also protected the production parts from damage. The company estimates that it saved $160,000 in time and labor by making this switch.
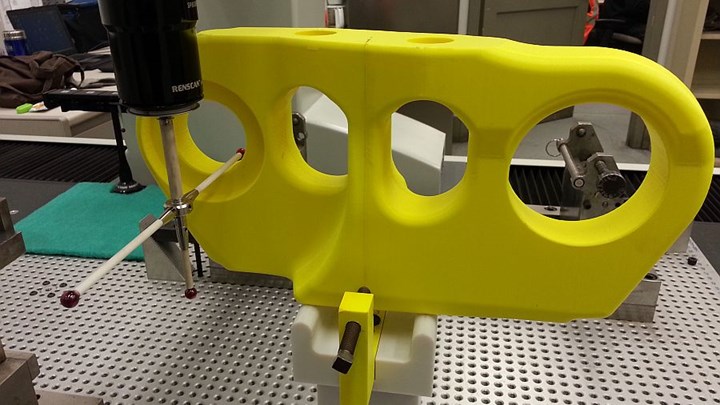
This lightweight model of a track link made from ABS polycarbonate allowed Caterpillar employees to set CMM programs without waiting for the heavy forged parts to arrive.
Related Content
Video: 5" Diameter Navy Artillery Rounds Made Through Robot Directed Energy Deposition (DED) Instead of Forging
Big Metal Additive conceives additive manufacturing production factory making hundreds of Navy projectile housings per day.
Read MoreHow Norsk Titanium Is Scaling Up AM Production — and Employment — in New York State
New opportunities for part production via the company’s forging-like additive process are coming from the aerospace industry as well as a different sector, the semiconductor industry.
Read MoreAt General Atomics, Do Unmanned Aerial Systems Reveal the Future of Aircraft Manufacturing?
The maker of the Predator and SkyGuardian remote aircraft can implement additive manufacturing more rapidly and widely than the makers of other types of planes. The role of 3D printing in current and future UAS components hints at how far AM can go to save cost and time in aircraft production and design.
Read MoreAdditive Manufacturing Is Subtractive, Too: How CNC Machining Integrates With AM (Includes Video)
For Keselowski Advanced Manufacturing, succeeding with laser powder bed fusion as a production process means developing a machine shop that is responsive to, and moves at the pacing of, metal 3D printing.
Read MoreRead Next
Bike Manufacturer Uses Additive Manufacturing to Create Lighter, More Complex, Customized Parts
Titanium bike frame manufacturer Hanglun Technology mixes precision casting with 3D printing to create bikes that offer increased speed and reduced turbulence during long-distance rides, offering a smoother, faster and more efficient cycling experience.
Read MoreCrushable Lattices: The Lightweight Structures That Will Protect an Interplanetary Payload
NASA uses laser powder bed fusion plus chemical etching to create the lattice forms engineered to keep Mars rocks safe during a crash landing on Earth.
Read MoreAlquist 3D Looks Toward a Carbon-Sequestering Future with 3D Printed Infrastructure
The Colorado startup aims to reduce the carbon footprint of new buildings, homes and city infrastructure with robotic 3D printing and a specialized geopolymer material.
Read More
.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)