"Stereolithography for Metals" Produces Detailed Parts
Lithography-based Metal Manufacturing (LMM), a new technique developed by Incus uses a curing process based on stereolithography to build green metal parts with photopolymer.
Share
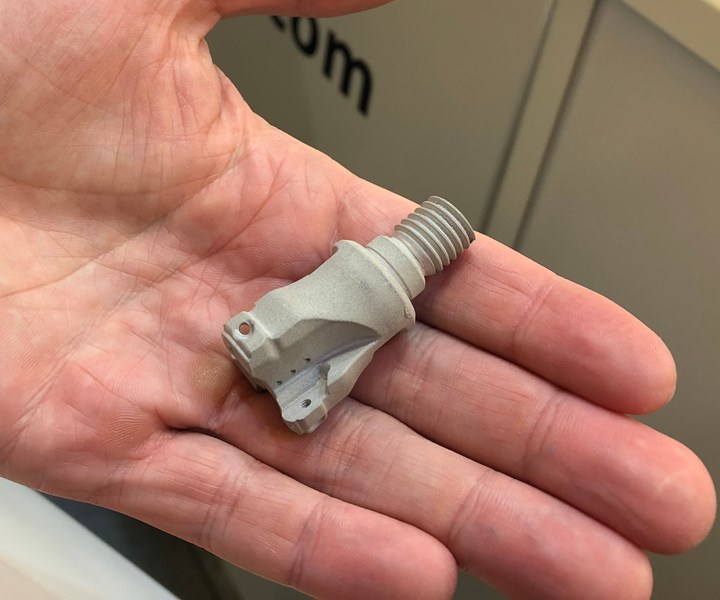

A new process developed by Incus promises the fine detail of stereolithography with any metal that can be sintered. (See this coolant-through cutting tool and more in our video roundup of “cool parts” from Formnext 2019.)
Stereolithography and similar resin-based 3D printing processes are known for building detailed, high-resolution parts in polymer. Now, Incus is leveraging many of the same benefits for metals, with a new process that combines photopolymer resin and metal powder.
Incus, a spinout from ceramics 3D printing company Lithoz, unveiled its Lithography-based Metal Manufacturing (LMM) process at Formnext 2019. Dr. Gerald Mitteramskogler, CEO, explained the process to me.
The key to LMM is its feedstock: photopolymer resin filled with metal powder. Unlike most SLA resins that are liquid during the printing process, this material remains solid but spreadable within the 20°C build chamber. “It’s a consistency like butter,” Mitteramskogler says.
A blade spreads the stock over a heated build plate. The photopolymer is cured with a digital light projection (DLP) engine to form each layer.
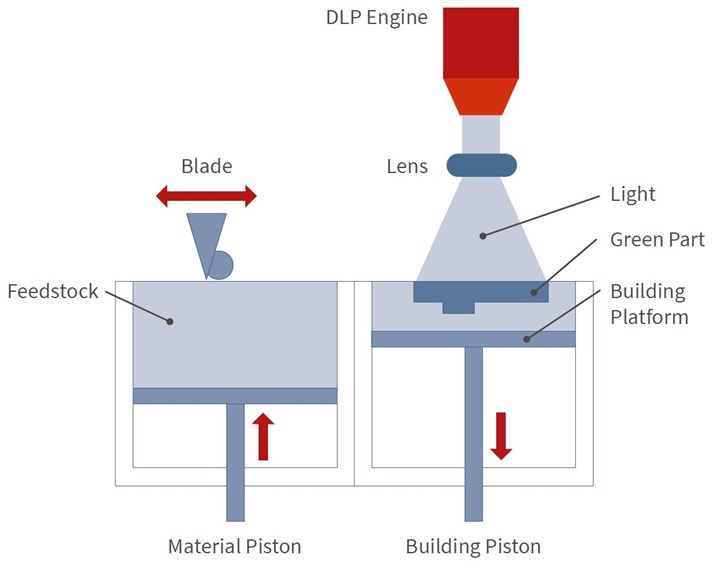
The spreadable feedstock is cured with light, similar to stereolithography, in a process that resembles powder bed fusion or binder jetting. Image: Incus
The polymerized green parts emerge from the printer in a block of material; an infrared light can be used to liquify the uncured material and quickly free them.
From there, the process looks more like binder jetting. Green polymerized parts are debound and sintered in a regular metal injection molding (MIM) furnace. The quality of LMM parts is similar to those made via MIM, with the benefits of the geometric freedom and speed enabled by 3D printing.

Similar to binder jetting, Lithography-Based Metal Manufacturing is suitable for small, finely detailed parts such as dental brackets, hinges for glasses, jewelry and watch faces like the one shown here.
Incus currently has four beta printers in the field, printing with 316L stainless steel. Additional materials are in development including titanium, tungsten, copper and precious metals. Lithography-based Metal Manufacturing is possible with any metal that is sinterable, Mitteramskogler says.
8 Cool Parts from Formnext 2019
Editors Peter Zelinski and Stephanie Hendrixson round up some of the coolest parts they spotted at Formnext 2019. See the cutting tool pictured above and more in this special edition of The Cool Parts Show. WATCH
Related Content
-
Louisville Slugger Uses Formlabs Technology to Accelerate Innovation
Louisville Slugger relies on Formlabs’ Form 3 stereolithography 3D printer to create both prototypes and manufacturing aids for designs of the composite and aluminum bats swung by youth and collegiate players.
-
NanoOne Green 3D Printer Offers Increased Precision, Ability to Work With Broad Range of Materials
Formnext 2024: The printer features UpNano’s adaptive resolution technology, which dynamically expands the width of the laser beam tenfold to speed up printing in bulk material areas or shrinks it where precision is needed.
-
Formlabs’ Form 4 3D Printer Offers New Levels of Reliability and Speed for Stereolithography
The Form 4 is designed to deliver most parts in less than two hours, offering users a powerful, affordable tool to bring ideas to life at fast speeds with excellent reliability, print quality and ease of use.
.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)



