Video: Robot Machining Will Complement Robot DED
Robots can do additive manufacturing. Can they do hybrid manufacturing? Precision milling of metal using a robot offers this promise.
Share
Read Next
At IMTS – The International Manufacturing Technology Show, part of what I was looking for were developments outside the show’s additive manufacturing area that have implications for AM. I found one in Kuka’s booth. The robot technology supplier was showcasing not only robotic 3D printing solutions, but also robotic metalcutting: CNC machining using the robot for milling metal. Improved robot rigidity makes this possible, along with a robot design allowing for high-force work. The promise: Directed energy deposition (DED) metal 3D printing via robot could be performed in a hybrid cycle, with the robot itself also taking care of the machining.
Transcript
Robots and additive manufacturing go together; do robots and hybrid manufacturing go together?
I am at IMTS, the International Manufacturing Technology Show, Chicago, Illinois. This is Kuka’s booth. Kuka, robot technology supplier. Additive manufacturing is one of the applications that they’re showcasing, showing how the path accuracy of their robots is capable of precise 3D printing of large forms in polymer and metal through directed energy deposition. But for harder materials like metal, can the robot also do subtractive operations, machining to bring the additive part closer to completion within the same cycle?
I would have said no, a robot is not precise enough for precision CNC machining. But Kuka pointed out robot rigidity has improved, so this robot takes advantage of that rigidity combined with shorter linkages between axes for even greater rigidity to realize this robotic metal machining solution developed by Robotics Solutions, robot integrator in Wisconsin.
Now, we are at a trade show, so this is not fully bolted down. The cutting that we’re showing here, it is light, but in a real production setting, the robot could be cutting aluminum, which is shown here, at twice the speed and a much heavier depth of cut and could do metals harder than aluminum as well. This is not as accurate as a CNC machining center, but it is easily precise enough for rough machining.
One user of this system, a foundry, uses a robot just like this as a low cost solution for rough machining of castings cheaper than doing the work on a machining center. This development is very complementary to robotic additive manufacturing in metal through DED because integrating machining like this on a robot means potentially a large metal part could be made through DED and might not need to be sent away for follow up machining or at the very least, much less machining would need to be done in another setup downstream. Instead, the DED could be done on a rigid robot like this one, a robot that is also capable of doing CNC milling as part of the same hybrid additive subtractive process.
Related Content
3D Printing for Job Shops: Part of Elevate Job Shops Series at IMTS
A half-day workshop at the International Manufacturing Technology Show helps job shops explore the many potential ways 3D printing technologies support and enhance machining.
Read MoreInnovation is Revving Up: ‘Manufacturing Explorers’ Season 3
Buckle up and join Max and Travis as they talk about the thrills of visiting innovative automotive companies in the premiere of their third and final season of “Manufacturing Explorers,” an IMTS+ original series.
Read MoreVideo: Scanning for Fast Model Capture and Validation of AM Parts
3D printing offers a fast way to obtain a part. Can developing the printable file and validating the printed part be done rapidly as well? See fast measurement technology for complex 3D forms I found at IMTS.
Read More3D Printing Solutions to Support Investment, Sand Casting
3D Systems is highlighting a design strategy for better investment casting patterns, as well as a new machine suitable for the production of patterns for sand casting.
Read MoreRead Next
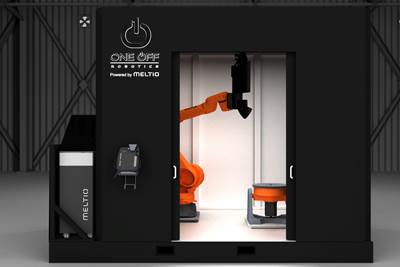
Meltio, One Off Robotics Develop Robotic AM Work Cell for Cost-Effective, Reliable Metal Part Production
The system offers a deposition rate of up to 1 kg/hr to create clean parts that are fully dense and mechanically equivalent or superior to those created from traditional manufacturing.
Read MoreCrushable Lattices: The Lightweight Structures That Will Protect an Interplanetary Payload
NASA uses laser powder bed fusion plus chemical etching to create the lattice forms engineered to keep Mars rocks safe during a crash landing on Earth.
Read MoreAlquist 3D Looks Toward a Carbon-Sequestering Future with 3D Printed Infrastructure
The Colorado startup aims to reduce the carbon footprint of new buildings, homes and city infrastructure with robotic 3D printing and a specialized geopolymer material.
Read More