The New Normal? Resilient Supply Chains with 3D Printing
We were already headed toward expanded adoption of 3D printing, in HP’s view, when the coronavirus hit. The pandemic’s disruption will only get us there faster.
The pandemic hasn’t slowed or derailed the adoption of 3D printing, in HP’s view. Instead, it has been an accelerator. Photos: HP
In a press briefing held June 3, HP’s Ramon Pastor, interim director of its 3D printing and digital manufacturing business, called the coronavirus pandemic a “watershed moment” for additive manufacturing (AM).
He was referring not only to 3D printing’s response to calls for PPE and testing swabs, but also to how and why this technology came to be applied for these items. Where the conventional supply chain broke down, 3D printing was able to step in, rapidly develop and earn approval for designs, distribute part files, and get production moving not in months and years, but days and weeks — timelines “previously unheard of” for healthcare. Simultaneously, AM was being applied to produce other needed items in supply chains not directly related to the pandemic, but disrupted by it all the same.
“The pandemic has been an accelerant for the trajectory of the industry.”
“The pandemic has been an accelerant for the trajectory of the industry,” Pastor says. “During this time, additive manufacturing did one of two things: it enabled companies to keep their existing production operational or it allowed them to pivot to creating essential products.” But, he points out, “The ability to do either of those things with 3D printing existed before COVID-19, so it is not a change of course. What it is, is a proof point like no other.”
3D Printing Will Shore Up Supply Chains in the New Normal

Ramon Pastor leads HP’s 3D Printing and Digital Manufacturing business as interim president.
The lessons learned from this crisis period will not end with the flattening of the curve; HP expects that processes and knowledge proved out as a result of coronavirus will inform and shape the future of manufacturing.
“We have seen the limits of the traditional supply chain,” as a result of this crisis Pastor says. “Now, we morph to the ‘new normal times’ knowing and realizing what we have accomplished will inform a new way to work — and not just in medical.” The test now, he says, is to build resilient supply chains that, yes, can benefit from 3D printing.
“Prior to COVID-19, much of the supply chain conversation and the evolution toward digital supply chains was focused on efficiency and transparency,” Pastor says. “Those priorities have not gone away; in fact, they are more important than ever. But another element has now come to the forefront of supply chain transformation, and that is risk mitigation. 3D printing has been so important in this crisis is because it is inherently digital, localized and sustainable, making it more immune to economic or geopolitical volatility. ”
New Services Support Scaling with Additive Manufacturing
Several of the company’s new technology announcements and business developments speak to this, with new services for manufacturers who are perhaps turning to additive for the first time, having seen its flexible, agile response during the crisis. HP has introduced a suite of 3D Professional Services to help AM users of all levels quickly scale to production.
At the initial adoption level, a digital Parts Assessment tool and consulting services will help customers analyze and identify which parts may be candidates for the company’s Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) polymer 3D printing technology. Design for additive manufacturing (DFAM) training will also be available. For users ready to develop their AM applications, HP offers design optimization as well as services to build out postprocessing procedures, quality assurance and other processes. When manufacturers are at the moment of moving into volume production, they can utilize HP expertise to work with their suppliers or develop an in-house production process if vertically integrated.

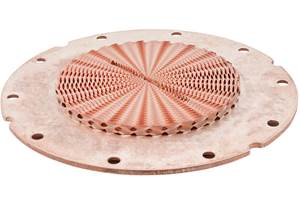
Applications for Multi Jet Fusion in the automotive space, such as this door defroster, are expected to expand with the introduction of HP 3D High Reusability PP enabled by BASF.
At a partnership level, HP also announced new and expanded relationships during the June 3 call. The company is working with Germany-based Oeschler to prove out new applications for its technologies in the automotive, home and medical spaces. Chicago-based service bureau Fast Radius has joined the Distributed Manufacturing Network, a collection of production-scale 3D printing companies that provide manufacturing services. And HP’s ongoing collaboration with materials manufacturer BASF has resulted in a new polymer material for MJF, polypropylene (PP).
“The current pandemic will not be the last profound global challenge we face.”
But as additive manufacturing marches forward, HP’s focus is not just on increasing applications and material options. It sees 3D printing not in a vacuum, but as part of an interconnected and dynamic ecosystem.
“The current pandemic will not be the last profound global challenge we face,” Pastor says. Being resilient in the face of future emergencies will not only mean having duplicate facilities or redundant resources; supply chains will also need to rely on production assets that are flexible and agile, a role that digital and additive manufacturing can fill.
Related Content
Video: 5" Diameter Navy Artillery Rounds Made Through Robot Directed Energy Deposition (DED) Instead of Forging
Big Metal Additive conceives additive manufacturing production factory making hundreds of Navy projectile housings per day.
Read MoreHow Norsk Titanium Is Scaling Up AM Production — and Employment — in New York State
New opportunities for part production via the company’s forging-like additive process are coming from the aerospace industry as well as a different sector, the semiconductor industry.
Read MoreWith Electrochemical Additive Manufacturing (ECAM), Cooling Technology Is Advancing by Degrees
San Diego-based Fabric8Labs is applying electroplating chemistries and DLP-style machines to 3D print cold plates for the semiconductor industry in pure copper. These complex geometries combined with the rise of liquid cooling systems promise significant improvements for thermal management.
Read MoreBeehive Industries Is Going Big on Small-Scale Engines Made Through Additive Manufacturing
Backed by decades of experience in both aviation and additive, the company is now laser-focused on a single goal: developing, proving and scaling production of engines providing 5,000 lbs of thrust or less.
Read MoreRead Next
In Coronavirus Uncertainty, 3D Printing Is a Potential Solution for U.S. Manufacturing
The impact of the COVID-19 virus has reached U.S. manufacturers by way of the supply chain. Here are several ways 3D printing could help, plus a video discussion of the data with economist Michael Guckes.
Read MoreWhy HP Believes in 3D Printing
The reasons go beyond the world of manufacturing. Ramon Pastor, global head of plastics solutions for 3D Printing and Digital Manufacturing, shares the four macrotrends at the foundation of HP’s 3D printing business.
Read MoreCrushable Lattices: The Lightweight Structures That Will Protect an Interplanetary Payload
NASA uses laser powder bed fusion plus chemical etching to create the lattice forms engineered to keep Mars rocks safe during a crash landing on Earth.
Read More
.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)