Reinforced Polymer 3D Printing, Adjustable on the Fly
With Continuous Kinetic Mixing (CKM), 3DFortify sees expanded possibilities for printing polymer composites reinforced with fibers, ceramics and even metal flake in any concentration needed.

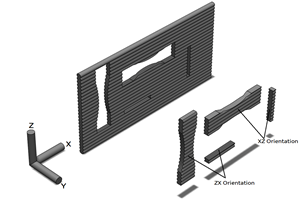
This demo part illustrates DCM’s filler alignment capabilities, compatible with a growing range of additives. The plastic is filled with steel flake (less than 3% by volume) throughout. The “F” is formed by orienting these flakes along the X-Y plane; in the more transparent areas, the flakes are aligned with the Z axis.
Reinforced 3D printing typically refers to filament or pellet extrusion systems, where a print head lays a reinforcing fiber along with the plastic or extrudes material containing chopped filler. The strategy is not usually associated with resin-style 3D printers that use stereolithography or digital light processing (DLP) to cure the material. Why? The main challenge comes down to the nature of the feedstock: chopped fibers and other fillers are liable to sink in liquid resin, making it difficult to ensure the necessary blend of material.
3DFortify has created a solution to solve this problem for its “Fluxprint" DLP-based 3D printing platform, which is capable of aligning tiny fillers within the resin during the build. What the company is calling a Continuous Kinetic Mixing (CKM) unit built into the printer mixes and then maintains the proper blend of additives within the photopolymer resin. The resin and fillers are kept separate until combined by the system, in the fill percentage required by the application. Aside from the new possibilities CKM brings for DLP-based 3D printing of composite materials, another notable benefit is this: The cartridge-based system simplifies material handling and allows for reloading while the print continues.
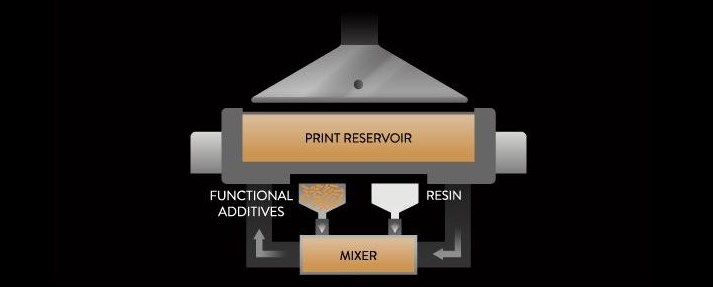
The resins and additives are kept separate with the CKM system, allowing operators to change the amount of fill on the fly.
“CKM has the ability to extend print life without having a user go in to monitor print levels, glove up, weigh out resin, and pour it into the reservoir,” says Josh Martin, 3DFortify co-founder and CEO. “If you have a resin you need to shake up that’s only good for 8 hours, for example, the system can meter and mix it while the printer is going. You can also use it to tailor formulations on the fly.”

The Fluxprint DLP system will begin shipping to customers this summer.
When we first reported on the company’s Digital Composite Manufacturing (DCM) technology, the emphasis was on carbon fiber- and glass-filled polymers, primarily for mold tooling. Molds are still a core focus for the company, but automated mixing and adjustable fill capability is becoming more important as DCM’s usefulness diversifies. 3DFortify and its customers are now pursuing applications requiring heavier fillers like ceramics and metallics used in greater density, such as electrostatic discharge (ESD) compliant tooling, electromagnetic devices and sintered ceramics.
“For the material to reach its goals in these applications, it has to be heavily loaded,” Martin says. “We’re talking almost half of the volume of a liter of resin being the ceramic particles, which are four to six times the density of the resin.”
The mixing capability that makes this possible would have premiered at AMUG 2020, but given the circumstances 3DFortify opted to make the CKM announcement digitally. The company still plans to go forward with the launch of its Fluxprint platform, which is expected to begin shipping to customers by the end of June.
Related Content
3D Printed Preforms Improve Strength of Composite Brackets: The Cool Parts Show Bonus
On this episode, we look at a pin bracket for the overhead bin of an airplane made in two composite versions: one with continuous fiber 3D printed reinforcements plus chopped fiber material, and one molded from chopped fiber alone.
Read More3 Unique Elements of LFAM to Consider in Design
While similar to desktop fused filament fabrication (FFF), large format additive manufacturing (LFAM) in polymer composite poses several unique challenges as a result of its scale.
Read MoreAdvancing Additive Manufacturing With a CATCH and Release Approach
Solutions for energy efficiency, sustainability, part repair and more are developing at Siemens’ Charlotte Advanced Technology Collaboration Hub (CATCH) in North Carolina.
Read MoreEvaluating the Printability and Mechanical Properties of LFAM Regrind
A study conducted by SABIC and Local Motors identified potential for the reuse of scrap reinforced polymer from large-format additive manufacturing. As this method increases in popularity, sustainable practices for recycling excess materials is a burgeoning concern.
Read MoreRead Next
Magnetic 3D Printing with Fiber Reinforcement Fills Tooling Gap
Fortify’s Digital Composite Manufacturing (DCM) platform pairs high-performance resins with fiber reinforcement that can be controlled at the voxel level. The process promises a faster route to durable injection mold tooling.
Read MoreBike Manufacturer Uses Additive Manufacturing to Create Lighter, More Complex, Customized Parts
Titanium bike frame manufacturer Hanglun Technology mixes precision casting with 3D printing to create bikes that offer increased speed and reduced turbulence during long-distance rides, offering a smoother, faster and more efficient cycling experience.
Read More3D Printed Polymer EOAT Increases Safety of Cobots
Contract manufacturer Anubis 3D applies polymer 3D printing processes to manufacture cobot tooling that is lightweight, smooth and safer for human interaction.
Read More
.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)