Mantle’s High-Precision Shaping for Automating Precision Toolmaking
The High-Precision Shaping feature expands the capabilities of Mantle’s hybrid metal 3D printing technology, enabling finer feature creation and dramatically expanding the geometries compatible with its TrueShape process.
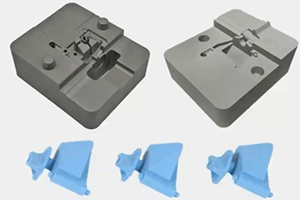
Mantle’s High-Precision Shaping package prints features that would require extensive EDM to produce via traditional manufacturing. Photo Credit: Mantle
Mantle, a provider of metal 3D printing for toolmaking, has updated its TrueShape Software with new High-Precision Shaping capabilities, as it continues to deliver a turn-key system with no CAM programming required. The High-Precision Shaping package includes 0.006" and 0.010" ball mill cutting tools and automated toolpathing software.
The package expands the capabilities of Mantle’s hybrid metal 3D printing technology, enabling finer feature creation and dramatically expanding the geometries compatible with its TrueShape process. It also enables tool rooms to automate their toolmaking process by producing sharp corners and edges without requiring EDM operations.
The new cutting tools (including the .006” and .010” ball mill cutting tools) enable radii under 0.003", which is comparable to sinker EDM. By eliminating EDM and other toolmaking operations, Mantle says it helps tool rooms reduce the time required to produce mold tools by up to 75%.
“At Mantle, our goal is to help tool rooms increase the number of complex mold tools they produce while reducing the time, cost and labor to produce them,” says Ted Sorom, Mantle CEO and co-founder. “By deploying our new High-Precision Shaping capabilities, our customers can produce steel tools faster than ever — without requiring programming, setup and operator time from overworked toolmakers.”
Mantle says its TrueShape technology combines 3D printing of its tool steel pastes with traditional CNC machining to refine the shape of printed tools and deliver accuracy, surface finish and tool steel properties unmatched in the metal 3D printing industry. Mantle’s 3D printer is built on a trusted CNC platform and utilizes multiple cutting mills to refine the shape of the printed tool while it is still in a soft state. The new High-Precision Shaping package enables tool rooms to produce tools with radii under 0.003", a 70% improvement compared to the .010" radii previously attainable, thereby eliminating more of the costly and time-consuming EDM operations of traditional toolmaking.
“Mantle allows us to offer production-grade tooling to our customers in prototype time,” says Eric Derner, technical sales applications engineer at Nicolet Plastics, an injection molder. “Mantle will allow us to reduce our need for offshore tooling, which introduces scheduling and supply chain risk, with comparable pricing. With Mantle’s H13 tool steel and new High-Precision Shaping capabilities, we can print tools in-house and deliver complex molded parts to our customers weeks faster than before.”
-
Watch this video about Mantle’s 3D printing technology which enabled moldmaker Westminster Tool to go from design to injection-molded prototype medical parts in three weeks.
-
Learn how Mantle’s P-200 printer and F-200 furnace metal 3D printing technology for toolmaking are said to simplify the way mold tool components are made and accelerate how manufacturers make molded parts, speeding the process of going from product idea to launch.
-
This video shows how PepsiCo used Mantle’s Hybrid 3D printing process to make blow molds for bottles.
- A recent webinar explored Nicolet Plastics’ success using Trueshape Technology to print injection mold tooling, as this method effectively reduced lead times and cost constraints, while producing better inserts.
Related Content
Video: Hybrid Manufacturing Without Melting: Hermle’s Metal Powder Application (MPA) Process
The Metal Powder Application (MPA) process uses cold spray to apply metal to an existing workpiece. Because the material deforms rather than melts, MPA opens new possibilities for functional grading and other multimaterial applications.
Read MoreMachine Tool Drawbar Made With Additive Manufacturing Saves DMG MORI 90% Lead Time and 67% CO2 Emission
A new production process for the multimetal drawbar replaces an outsourced plating step with directed energy deposition, performing this DED along with roughing, finishing and grinding on a single machine.
Read MoreNew Equipment, Additive Manufacturing for Casting Replacement and AM's Next Phase at IMTS 2024: AM Radio #54
Additive manufacturing’s presence at IMTS – The International Manufacturing Technology Show revealed trends in technology as well as how 3D printing is being applied today and where it will be tomorrow. Peter Zelinski and I share observations from the show on this episode of AM Radio.
Read MoreNicolet Plastics Succeeds Using Mantle's Hybrid Metal 3D Printing Method for Mold Tooling
A recent webinar explores Nicolet Plastics’ success using Trueshape Technology, Mantle’s approach to print injection mold tooling. The current challenges this technology addresses and alleviates in additive manufacturing confirms this method is effectively reducing lead times and cost constraints, while producing better inserts.
Read MoreRead Next
Crushable Lattices: The Lightweight Structures That Will Protect an Interplanetary Payload
NASA uses laser powder bed fusion plus chemical etching to create the lattice forms engineered to keep Mars rocks safe during a crash landing on Earth.
Read MorePostprocessing Steps and Costs for Metal 3D Printing
When your metal part is done 3D printing, you just pull it out of the machine and start using it, right? Not exactly.
Read More3D Printed Polymer EOAT Increases Safety of Cobots
Contract manufacturer Anubis 3D applies polymer 3D printing processes to manufacture cobot tooling that is lightweight, smooth and safer for human interaction.
Read More