Video: Miniature Jet Engine Made with Additive Manufacturing
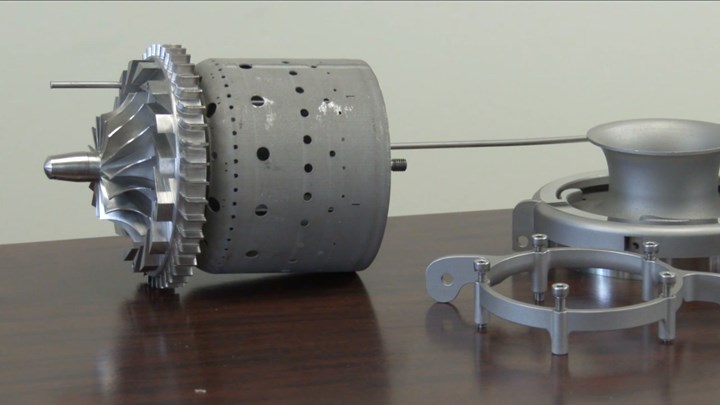
GE engineers started with a radio-controlled engine and redesigned it for additive manufacturing. This model manufacturing exercise illustrates important real points about additive manufacturing as a production option.
GE produced this video about a working jet engine model that was created through additive manufacturing and run in a GE Aviation test cell. The video briefly documents the manufacturing process that produced in this engine, a process that illustrates at least two significant points related to additive manufacturing. They are:
1. Design freedom. Because it makes parts that machining can’t produce, additive manufacturing offers the opportunity to reengineer parts and assemblies for greater performance. GE’s engineers started with a radio-controlled aircraft engine, but then they improved its components for additive manufacturing. (They also further improved them by making them from high-temperature alloys a radio-controlled engine wouldn’t normally use.)
2. Secondary operations. Additive manufacturing makes intricate parts, but it does not necessarily make finished parts. The video shows this. The parts that were produced additively (on an EOS M270 machine) went on to receive secondary machining and finishing steps. The same will almost certainly be true of any production metal part made through additive manufacturing.
Related Content
-
Additive Manufacturing Is Subtractive, Too: How CNC Machining Integrates With AM (Includes Video)
For Keselowski Advanced Manufacturing, succeeding with laser powder bed fusion as a production process means developing a machine shop that is responsive to, and moves at the pacing of, metal 3D printing.
-
3D Printed Titanium Replaces Aluminum for Unmanned Aircraft Wing Splice: The Cool Parts Show #72
Rapid Plasma Deposition produces the near-net-shape preform for a newly designed wing splice for remotely piloted aircraft from General Atomics. The Cool Parts Show visits Norsk Titanium, where this part is made.
-
This Drone Bird with 3D Printed Parts Mimics a Peregrine Falcon: The Cool Parts Show #66
The Drone Bird Company has developed aircraft that mimic birds of prey to scare off problem birds. The drones feature 3D printed fuselages made by Parts on Demand from ALM materials.












