Webinar: Discovering Design Freedom and Mass Customization from the Electrification Revolution
The transition to electric vehicles is an exciting time to re-think car design, business models, and consider how to best deliver value. New tools and methods such as AI design and additive manufacturing are being leveraged to unlock unrealized potential.
Additive Electrified
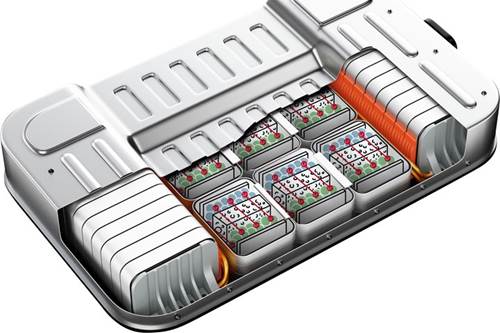
Electric vehicles (EVs) are reshaping transportation, but they are also changing vehicle production. EVs represent totally new product platforms for established manufacturers, and in many cases are being brought to market by brand-new companies.
Electrification brings a blank slate to the manufacturing process, providing inroads for additive manufacturing (AM) to potentially fill production needs.

3D PRINTING FOR ELECTRIC VEHICLES PRESENTATION SERIES
HP WATCH NOW AUTODESK WATCH NOW
What Qualifies as an Electric Vehicle?
Simply put, an electric vehicle or EV is any vehicle that uses electric motors for propulsion. An EV can be powered by energy sources such as an onboard battery, solar energy or an electric current collector (think overhead wires for a trolley system). Hybrid vehicles combine an electric motor with another source of power, typically a gas- or diesel-powered engine.
While automotive is leading the charge to electrification, other kinds of vehicles that move people and/or products also fall under the EV category, including:
- battery-powered electric scooters;
- electric vertical take-off and landing (eVTOL) helicopters;
- electric trams and trains;
- solar-powered vehicles;
- autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs);
- next-generation electric aircraft;
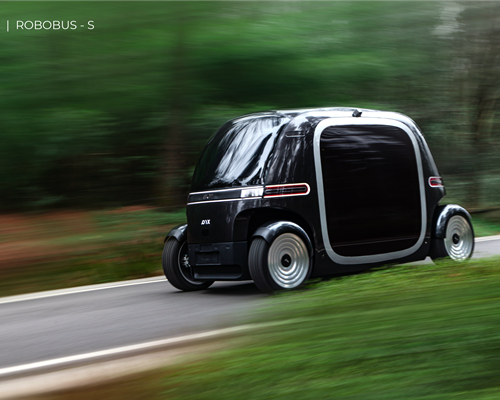
- autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs) for passengers or cargo;
- electrically powered spacecraft; and more.
What is Additive Manufacturing?
Additive Manufacturing is the production workflow that contains and depends on 3D printing technology. 3D printing is a step in that workflow, which also contains part design, build preparation, postprocessing, finishing and inspection. AM is not just a different type of production process; it demands and shapes different types of manufacturing enterprises.
AM Can Address EVs’ Challenges
EVs are generally more efficient than vehicles powered by internal combustion engines (ICEs) and produce fewer emissions; they can be limited, however, by range, weight of necessary components like batteries, and time needed to charge.
EV producers can leverage the design and material possibilities of additive manufacturing to answer these challenges, creating lighter weight, more efficient and aesthetically pleasing EVs.
5 Advantages of AM in EV Production
Makers of EVs are more free to break away from the stamping, casting, machining and injection molding processes that have traditionally built conventional vehicles driven by internal combustion.
Some of these next-generation transportation solutions will even require the capabilities that only additive can deliver.
Here are five advantages of using additive manufacturing in EV production.
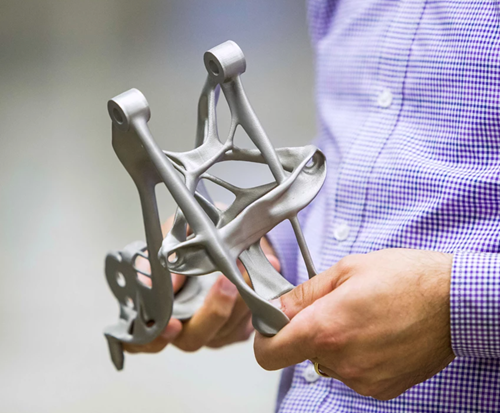
Advantage #1: Lightweighting
3D printing paired with generative design and topology optimization software solutions allows for the creation of components like brackets and connectors that use less material. Reduced weight in an EV can make room for a larger battery or more passengers, or extend the range of the vehicle. Weight is an important consideration for ground vehicles like cars and shuttles, but will be perhaps even more significant for next-generation electric aircraft.
Advantage #2: Use of innovative materials
AM is compatible with strong and lightweight materials such as aluminum which has become popular for car and truck frames in recent years. Additive manufacturing also makes solutions like carbon fiber-reinforced polymers more accessible; these composites can be a lighter and potentially more affordable alternative to metal parts. It is also possible to print materials such as copper for motor coils and lithium cobalt oxide (LCO) used in battery electrodes, bringing new possibilities to a vehicle’s powertrain.
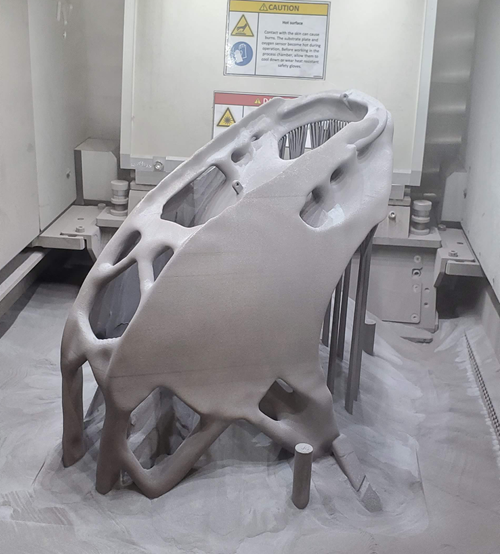
Advantage #3: Simplified manufacturing
3D printing enables the production of complex shapes, which can often replace larger assemblies. A heat exchanger for example can be printed in just one piece, in a design that works better than a conventional component and requires fewer process steps to obtain. Fewer parts also means easier assembly and less hand work necessary to produce new EVs.
Advantage #4: Customization and personalization
3D printing makes it affordable to manufacture customized aesthetic items like key fobs and badges, giving customers more choice over the appearance of their vehicles. Functional accessories and optional features can also be made this way, easily adapted to specific EVs or produced on demand only for customers who request it.
Advantage #5: Speed to market
3D printing has been used to prototype vehicles for decades, but is now suitable for many production parts as well. An EV manufacturer developing a new vehicle with AM in mind could move straight from prototyping to production as soon as the final design is reached. 3D printing need not deliver the final production part either — printed tooling used for cutting, stamping, forming, molding or casting EV components can provide similar benefits in terms of speed, geometric possibilities and functionality.
While AM’s impact on electric vehicles is still yet to be determined, 3D printing can be applied to many possible EV components:
Advancing EV through Additive
Additive manufacturing has gained ground in EV production in part because of the newness of these vehicles, but will continue to be important to their advancement.
Next-generation vehicles are coming that will be made possible only through the advantages that AM provides. 3D printing enables lightweighting, materials, optimized designs and more that will drive EVs even farther in the future.
EV Updates from Additive Manufacturing Media
8 Cool Parts From Formnext 2023: The Cool Parts Show #65
Peter Zelinski | Additive ManufacturingNew additive manufacturing technologies on display at Formnext were in many cases producing notable end-use components. Here are some of the coolest parts we found at this year’s show.
8 Transformations 3D Printing Is Making Possible
Stephanie Hendrixson | Additive ManufacturingAdditive manufacturing changes every space it touches; progress can be tracked by looking for moments of transformation. Here are 8 places where 3D printing is enabling transformative change.
What Does Additive Manufacturing Readiness Look Like?
Stephanie Hendrixson | Additive ManufacturingThe promise of distributed manufacturing is alluring, but to get there AM first needs to master scale production. GKN Additive’s Michigan facility illustrates what the journey might look like.
3D Printed Spares, Electrification and Cool Parts: Top 10 Stories of 2022: AM Radio #31
Stephanie Hendrixson | Additive ManufacturingOur top articles and videos from 2022 reflect increasing use of additive manufacturing for replacement parts; growing applications for electric motors; and a maturing user base. Read through the top 10 list or listen to the AM Radio podcast episode all about these stories.
How Aggressive EV Timelines Point to AM
Jodee McElfresh | Additive Manufacturing and CompositesWorldElectric vehicle sales are expected to grow significantly in the next decade. Additive manufacturing can help automakers fill their production needs.
Aluminum Gets Its Own Additive Manufacturing Process
Julia Hider | Modern Machine ShopAlloy Enterprises’ selective diffusion bonding process is specifically designed for high throughput production of aluminum parts, enabling additive manufacturing to compete with casting.
GE Sells Generator Technology for Stake in EV Startup
Angela Osborne | Gardner Business MediaThe company says the Karno generator is expected to be 20%+ more efficient than today’s leading generators — achieved by 3D printing of thermal components and innovative fuel-to-electricity conversion.
Sakuu Opens Silicon Valley Engineering Hub
Angela Osborne | Gardner Business MediaThe company says the engineering hub will advance its domestic battery printing initiatives and serve as a gateway for at-scale battery printing gigafactories globally.
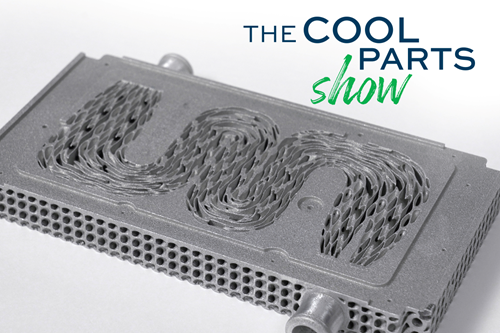
3D Printed Cold Plate for an Electric Race Car: The Cool Parts Show #51
Stephanie Hendrixson | Additive ManufacturingAn unconventional lattice design and biomimicry are key to the performance of this fluid-cooled heat exchanger for a battery-powered race car.
How Additive Manufacturing Is Transforming EVs and Transportation: AM Radio #23
Stephanie Hendrixson | Additive ManufacturingAs 3D printing is adopted into the electric vehicle (EV) market, it is not just vehicles that are being reshaped. In this episode of the AM Radio podcast, we discuss additive manufacturing and the future of transportation.
How GM Is Investing in Additive and EVs
Gary S. Vasilash | Gardner Business MediaPeople within the automaker aren’t just working with additive, they are actively promoting it to their colleagues throughout the organization.
New Electric Dirt Bike Is Designed for Molding, but Produced Through 3D Printing (Includes Video)
Peter Zelinski | Additive ManufacturingCobra Moto’s new all-electric youth motocross bike could not wait for mold tooling. Parts have been designed so they can be molded eventually, but to get the bike to market, the production method now is additive manufacturing.