Students Develop Design for Additive Manufacturing (DFAM) Worksheet for 3D Printing Success
A team of researchers at Purdue University developed and tested a DFAM worksheet to help novice and intermediate 3D printing users increase build success and minimize reprints.
There is a need recognized across the wide range of additive manufacturing users for guidelines to help manufacturers achieve success more quickly. Some such documentation does exist. But according to a paper written by engineering postdoctoral students at Purdue University, these guides tend to be impractical. They range from being too general to be useful to being too narrowly focused on a specific technology to be widely applicable.
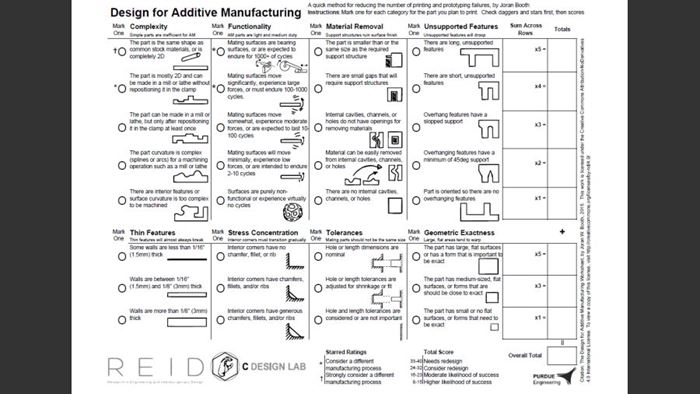
To begin to fill the knowledge gap they saw in design for additive manufacturing (DFAM), the authors of the paper developed a worksheet to help determine the manufacturability of designs destined for 3D printing. (Access a PDF version of this worksheet here.) This one-page document asks the user a series of questions about the design. Each possible response is assigned a point value. By totaling these points, the user arrives at a manufacturability score out of 40.
Intended for use by novice and intermediate AM users, the goal of the worksheet is ultimately to improve the chance of 3D printing success and reduce the need for reprints. It is not process-specific, focusing instead on the characteristics of the part such as feature support, stress concentration and tolerances. The illustrations for each response help to ensure accurate answers, but also suggest alternatives to problematic details.
To test the effectiveness of this DFAM worksheet, the researchers collaborated with the Boilermaker Lab, a high-volume 3D-printing facility serving the Purdue campus. With the help of the lab's monitors, researchers kept logs of prints made over the course of two months. For the first month, they tracked the number of failed builds and reprints without the use of the worksheet. During the second month, the worksheet was integrated into the workflow at the lab and researchers again tracked the failures and reprints during this time. All printers used in the study were MakerBot Replicators.
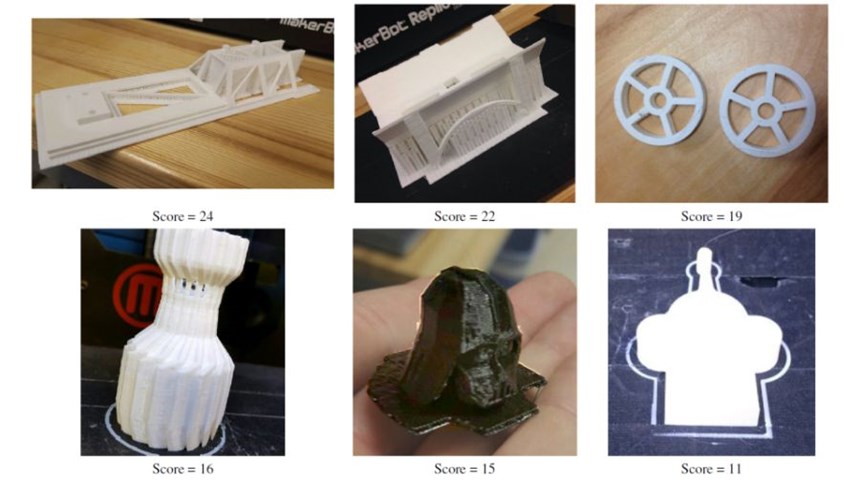
Over the course of the two months, 192 prints were completed without the worksheet, resulting in a failure rate of 19.8 percent and a reprint rate of 14.1 percent. After the DFAM worksheet was introduced, 36 prints were completed with the worksheet as part of the workflow. The rate of failure for these prints was 8.3 percent and reprint rate was 5.6 percent. Examples of parts made in the lab over the course of Month 2 can be seen in the second slide, above.
According to the researchers, the results of the study indicate a higher rate of success for novice and intermediate 3D printing users after using the worksheet. Along with recommending the use of this worksheet in academic and industrial environments, the team calls for future work focusing on the incorporation of recommender systems in CAD programs, suggesting that many of the principles measured in the worksheet could be detected automatically.
Related Content
-
Aircraft Ducts 3D Printed in Composite Instead of Metal: The Cool Parts Show #68
Eaton’s new reinforced PEKK, tailored to aircraft applications, provides a cheaper and faster way to make ducts compared to formed aluminum.
-
Possibilities From Electroplating 3D Printed Plastic Parts
Adding layers of nickel or copper to 3D printed polymer can impart desired properties such as electrical conductivity, EMI shielding, abrasion resistance and improved strength — approaching and even exceeding 3D printed metal, according to RePliForm.
-
What Does Additive Manufacturing Readiness Look Like?
The promise of distributed manufacturing is alluring, but to get there AM first needs to master scale production. GKN Additive’s Michigan facility illustrates what the journey might look like.

.jpg;width=70;height=70;mode=crop)